Car Alarms and Anti-Theft Systems
Do I really need a car alarm ?
Every 32 seconds, a vehicle is stolen somewhere in the United States. Automotive theft is big business-more than a million vehicles were stolen last year, along with untold numbers of auto stereos, batteries, tires, wheels, and valuables left in vehicle trunks. Even whole engines disappear in what is still referred to as "the midnight auto sale."Car Alarm Systems as low as $16.69 (02/2024)
CARLOCK Anti Theft Car Device • Real Time 4G Car Tracker & Car Alarm System • Carlock OBDHow Anti-Theft Systems Work
With the widespread and increasing rate of auto theft, automotive anti-theft systems have come into general use. Many auto manufacturers now offer anti-theft or alarm systems as optional equipment. In addition, there are literally dozens of after-market suppliers who manufacture these systems.
Most systems can be installed with hand tools in a few hours, but more complicated systems are best left to professionals.
There are two basic types of automotive anti-theft systems-alarm systems and movement inhibitors.
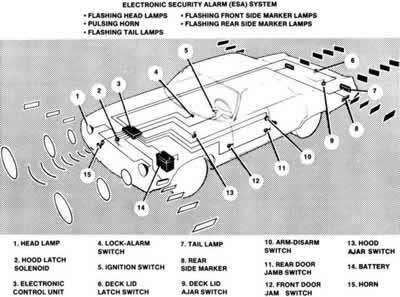
Fig. 1: Alarm systems cover all entry points of the vehicleALARM SYSTEMS
There are two basic types of burglar alarm systems for automobiles-those which actuate the vehicle horn, and those which set off an auxiliary siren or bell. Regardless of which type it is, each one can be broken down into its separate components: the trigger, trigger control and the alarm itself.
Fig. 3: Typical factory alarm systems use sophisticated electronics to monitor the vehicleTrigger Mechanisms
The trigger mechanism is the device used to activate the alarm. In most cases, the trigger consists of a switch or switches, and a drop relay. A drop relay is a relay that, once activated, will not recycle until reset manually; therefore, the alarm will not stop functioning even if the trigger switch is deactivated.
Motion sensitive switches such as mercury switches, pendulum switches, etc. are excellent means of detecting tampering. The switch may be mounted anywhere in the vehicle, and its sensitivity adjusted to the desired level. The disadvantage of a motion-sensitive switch is the accuracy with which it must be adjusted. The switch must respond to the opening of a door, the hood or trunk, but not to such things as parking on an incline, being bumped by a pedestrian, or traffic passing by. Once the proper sensitivity is determined, it is a good idea to include a timer in the trigger circuit, to shut the alarm off after a certain period if it is accidentally triggered.
Pushbutton switches (such as interior light doorjamb switches) mounted on all doors and the hood and trunk may be used to trigger an alarm. These spring-loaded, normally closed switches may be positioned adjacent to the existing switches on the doorjambs and on the hood and trunk latch plates. A combination system of motion sensitive and pushbutton switches will provide excellent protection. Mercury switches used to activate hood and trunk lights may be used as triggers, in lieu of pushbutton switches, on the hood and trunk.
Trigger Control Switches
The trigger control switch acts as an on-off switch for the alarm system. It must be arranged in such a manner so that the owner may enter the vehicle without triggering the alarm, but a thief must be unable to detect or disarm it.
The simplest type of control switch is a toggle switch mounted outside the vehicle in an inconspicuous place. Inside the fender well or under the rocker panel are two typical places that this type of switch is mounted. The only drawbacks to this type of switch are that the switch and wiring must be waterproofed, and that someone may find the switch and deactivate the alarm. The most popular type of switch is the locking type that may be mounted anywhere on the outside of the vehicle. These switches use cylindrical "pickproof" locks, and provide excellent protection, in addition to acting as a visual deterrent.
Alarms
An alarm may be devised as an integral part of the electrical system to set off the horn, or the warning system may contain its own alarm. To connect an alarm system utilizing the vehicle horn, proceed as follows: Locate the terminal on the horn relay that will sound the horn when it is bridged to ground. Connect one lead from the on-off switch to this terminal. Connect the other lead from the on-off switch to a pulsating (flasher-type) terminal. Connect the open terminal of the pulsating switch to the trigger mechanism. Now firmly ground the trigger mechanism.
Non-integral, self-contained alarm systems may be connected to the accessory position in the fuse box. The alarm itself (siren, bell, buzzer, etc.) must be loud enough to attract attention at a reasonable distance, and should be positioned somewhere where full advantage can be taken of its capabilities (such as behind the grill). A drop relay and/or a timer should be installed somewhere in the circuit. The drop relay will keep the alarm activated, even after the trigger is deactivated, unless all current is removed from the alarm circuit. The timer is used to deactivate the alarm a certain period after the trigger is deactivated, to prevent the alarm running down the battery, and to prevent disturbing the peace after accidental triggering. By installing a alarm system to your vehicle, you can drastically reduce your car insurance.
One of the best things you can do after you install one of these alarm systems is to mount the "protected by alarm" sticker that comes with the system. A casual thief seeing this sticker isn't going to stick around to see if it's telling the truth or not.